4. Reaction Quotient Q
The progress of a chemical reaction can be expressed by the reaction quotient Q.
a A + b B  c C + d D
c C + d D
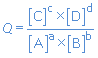
At the start of the reaction, the concentrations of A and B are maximal and the concentrations of C and D are equal to zero (there is no C and D formed yet). So at the start the reaction quotient is zero: Q = 0.
During the reaction the concentrations of A and B are decreasing and the concentrations of C and D are increasing. So the reaction quotient Q is increasing.
When the reaction is completed, the concentrations of A and B are equal to zero (there is no A and/or B left) and the concentrations of C and D are maximal. So when the reaction is completed the reaction quotient is infinite.
So, the reaction quotient Q is a number (between 0 and infinity) that tells us how far a chemical reaction is completed. Reactions with Q = 0 do not occur. Reactions with a very large Q proceed to completion.
Equilibrium reactions proceed until Q reaches a certain value, typical for the reaction. Once Q reaches that certain value, the equilibrium reactions seems to come to a standstill: the concentrations of all the reaction components stay constant. This situation is called the equilibrium state.
Summary
Reaction Quotient Q |
Indicates the progress of a reaction |
From 0 (no reaction) to infinity (reaction completed) |