8. pH of a Solution of a Weak Acid
When a weak acid like HOAc (acetic acid) is dissolved in water, only a few HOAc-molecules will donate a proton:
HOAc(aq) + H2O(l)  H3O+(aq) + Ac-(aq)
H3O+(aq) + Ac-(aq)
or
HOAc(aq)  H+(aq) + OAc-(aq)
H+(aq) + OAc-(aq)

[H3O+] or [H+] and pH of the solution can be calculated from Ka.
Let us calculate the pH of 0.1 mol/L HOAc.
|
HOAc |
H+ |
OAc- |
Beginning |
0.1 mol/L |
0 mol/L (*) |
0 mol/L |
D |
- x mol/L |
+ x mol/L |
+ x mol/L |
Equilibrium |
(0.1 - x) mol/L |
x mol/L |
x mol/L |
(*) The hydrogen ions delivered by the ionization of water are neglected. The weak acid HOAc (Ka = 1.8 x 10-5) is much stronger than the weak acid H2O (Ka = 1.0 x 10-14).
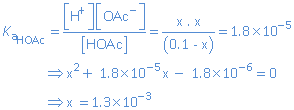
So we find at equilibrium: [H+] = 1.3 x 10-3 mol/L  pH = - log 1.3 x 10-3 = 2.88.
pH = - log 1.3 x 10-3 = 2.88.
pH + pOH = 14  pOH = 13.
pOH = 13.
Summary
pH of a solution of a weak acid HA in water
|
Calculate the concentrations in the equilibrium state
Calculate pH
|