Some species can react as an acid and as a base. This is the case for negative ions of polyprotic acids still containing hydrogen (NaHCO3 for instance):
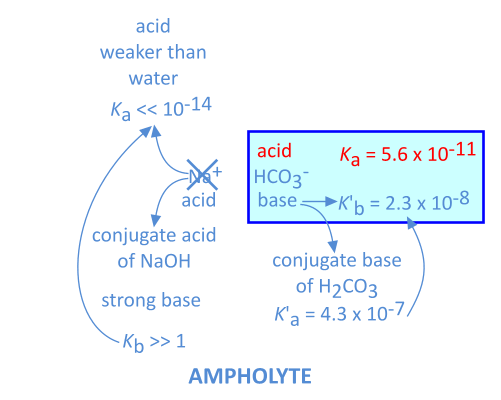

This is also the case for aminoacids (Glycine, H2N-CH2-COOH for instance), containing an acidic (-COOH) and a basic (-NH2) group:
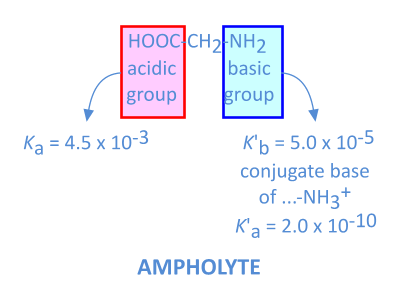

The pH of a solution of an ampholyte can be calculated, fairly accurate, by using the approximate formula:

Note that the pH of a solution of an ampholyte is independent of the concentration.